
Optical Transceiver Modules-Enabling High-Speed Optical Communication
Introduction:
In the era of modern information technology, the demand for high-speed and high-bandwidth data transmission is continuously growing. Optical communication technology has emerged as a key solution to meet these demands. At the heart of optical communication systems lies the optical transceiver module, playing a crucial role in enabling the conversion of optical signals to electrical signals and vice versa. This blog post aims to provide an overview of optical transceiver modules, including their definition, principles of operation, and application areas.
Definition and Principles of Operation:
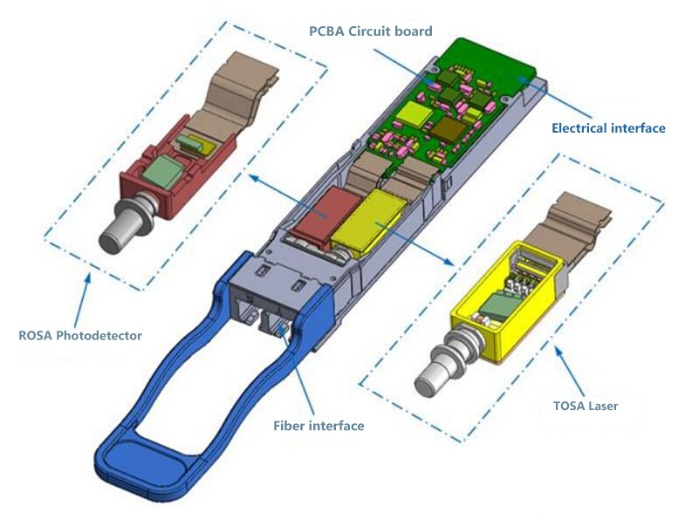
An optical transceiver module, also known as an optical module or transceiver, is a device used in optical communication systems to facilitate the conversion between optical and electrical signals. It typically consists of an optical transmitter and an optical receiver. The optical transmitter converts electrical signals into optical signals and transmits them through optical fibers. At the receiving end, the optical receiver receives the optical signals from the fiber and converts them back into electrical signals for further data processing and transmission.
The working principle of an optical transceiver module is relatively straightforward yet crucial. In the transmitter section, a laser diode or light-emitting diode (LED) is used to generate a narrow beam of laser light by exciting it with electrical current. This light represents the optical signal carrying data. The optical signal is then transmitted through optical fibers, following the properties of light, including attenuation and propagation. At the receiving end, the optical receiver employs a photodetector to convert the received optical signals back into corresponding electrical signals, facilitating subsequent electronic processing and data transmission.
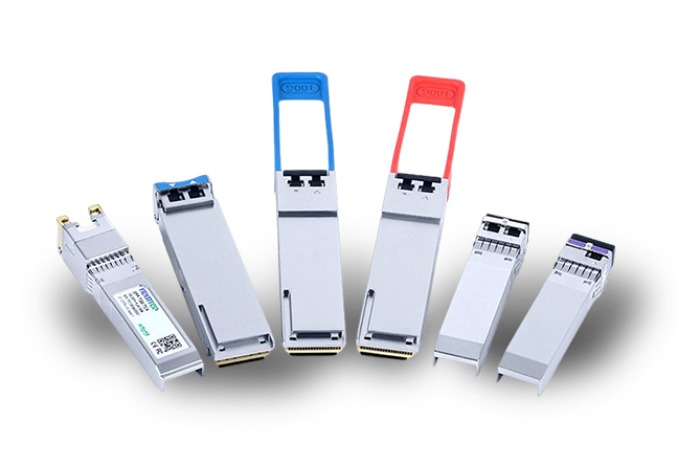

Application Areas:
Optical transceiver modules find extensive applications across various domains. Firstly, they play a vital role in optical fiber communication. Whether it's single-mode or multi-mode fiber, optical transceiver modules efficiently convert electrical signals into optical signals, enabling long-distance data transmission. Secondly, in the realm of data centers, optical transceiver modules are utilized for high-speed network connectivity, supporting rapid communication between servers within data centers and connecting data centers to external networks. Additionally, optical transceiver modules are widely used in wireless communication base stations, computer networks, and military communication, catering to the requirements of high-bandwidth and low-latency transmission in diverse scenarios.
Various types of optical transceiver modules are available, including SFP (Small Form-Factor Pluggable), QSFP (Quad Small Form-Factor Pluggable), CFP (C Form-Factor Pluggable), and CFP2/CXP (100G/400G C Form-Factor Pluggable), among others. Different module types offer varying transmission speeds and distances, such as 1G, 10G, 40G, 100G, and 400G. These modules adhere to standardized interfaces, ensuring interoperability and flexibility within optical networks.
Conclusion:
Optical transceiver modules are indispensable components of optical communication systems, converting electrical signals to optical signals and facilitating high-speed, high-bandwidth data transmission. Their applications span across optical fiber communication, data centers, wireless communication, and military communication fields. With ongoing technological advancements, optical transceiver modules will continue to evolve, providing even higher transmission speeds and longer transmission distances, ultimately enabling faster and more reliable network communication to connect the world.